ip
Lawrence User Guide
Lawrence is a chatbot designed to help you keep track of your tasks. It offers a myriad of features to ensure that your productivity is unaffected even when faced with high workloads.
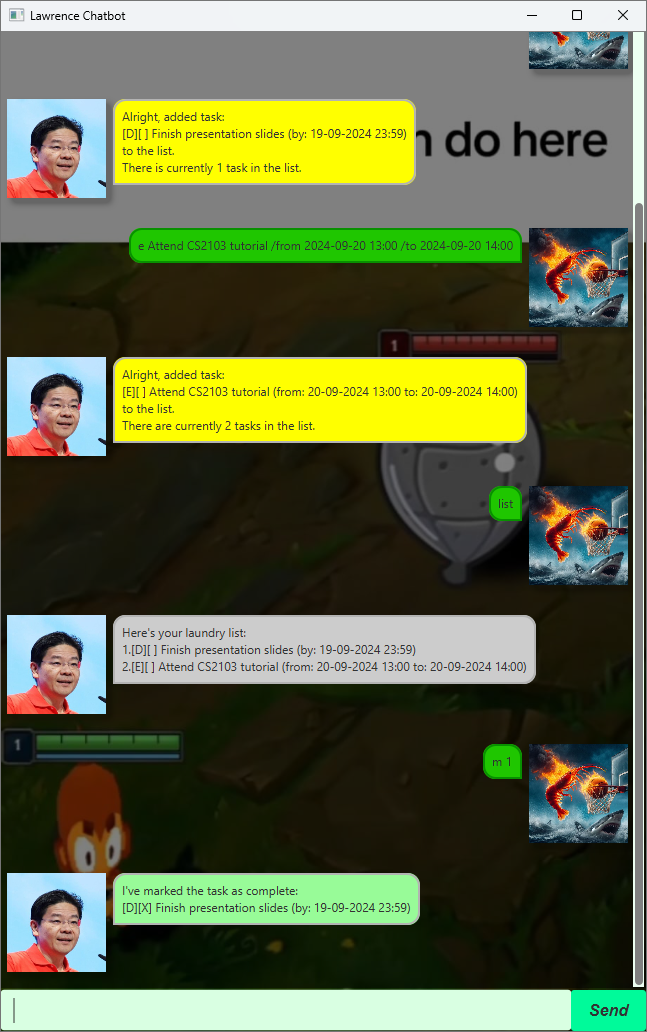
This is a list of features that Lawrence offers:
- Adding of Tasks
- Updating of Task Completion Statuses
- Deleting of Tracked Tasks
- Viewing Tracked Tasks
- Searching for Tasks using Keywords
Feature Usage
Adding Tasks
The bot is able to track 3 types of tasks: Todos, Deadlines and Events.
Adding Todos
Todos are the simplest of all tasks and are not associated with any time period.
To get Lawrence to track a todo, use the todo command.
Usage:
todo <todo-name>
If successful, the chatbot will respond with a readback of the added Todo.
Adding Deadlines
Deadlines are similar to Todos, but require an extra date parameter.
To get Lawrence to track a deadline use the deadline command.
Usage:
deadline <deadline-name> /by <date>
If successful, the chatbot will respond with a readback of the added Deadline.
Adding Events
Events are similar to Deadlines, but require a start date and end date.
To get Lawrence to track an Event, use the event command.
Usage:
event <event-name> /from <date> /to <date>
If successful, the chatbot will respond with a readback of the added Event.
Successful Add
If the command was executed successfully, the bot should respond with a readback of the added Task.
Alright, added <task-details> to the list.
There are currently <total-task-amount> task(s) in the list.
Unsucccessful Add
If there was any error when processing the task to be added, the bot will attempt to diagnose and inform you of the error in the command.
Updating Completion Statuses
Existing tasks can be marked as complete or incomplete using the mark and unmark commands respectively.
Usage:
mark <task-number>
unmark <task-number>
Examples:
mark 1will mark the first task in the list as completeunmark 2will mark the second task in the list as incomplete.
If the specified task number does not exist, the bot will not proceed with the request. Examples of invalid task numbers:
mark -1unmark 6when there are only5tasks in the list.
Deleting Tasks
Existing tasks can be deleted using the delete command with a specified task number.
Usage:
delete <task-number>
Example:
delete 1will delete the first task in the list.
If the specified task number does not exist, the bot will not proceed with the request. Examples of invalid task numbers:
delete -1delete 6when there are only5tasks in the list.
Viewing Tasks in the List
The tasks currently tracked by Lawrence can be viewed using the list command.
Usage:
list
Searching for Tasks
The tasks currently tracked by Lawrence can be searched by their descriptions.
To do so, use the find command.
Usage:
find <keyword-in-task-description>
The bot will consolidate and display the tasks that match the specified keywords.
Example: find organise will return all tasks that have the keyword organise in their task description.
If no matches are found, the bot will also notify you of the result.
Exiting the Program
To exit the program, use the bye command to terminate the chatbot session.
Usage:
bye
The tasks added are automatically saved and will persist between chatbot sessions.
Lenient Syntax
The bot is able to recognise some abbreviated commands to reduce the amount of typing the user needs to do. Commands can be recognised without fully spelling out the command.
Examples include:
tandtocan be recognised as thetodocommandmcan be recognised as themarkcommanducan be recognised as theunmarkcommand
Ambiguity
However, it should be noted that the delete and deadline command can be ambiguous if shortened to a single letter.
As such, the bot will refuse to process commands such as d as it may mean two different things.
Luckily, the bot is still able to recognise a slightly longer but still shortened form of these commands:
delis recognised asdeletedeadlis recognised asdeadline
Dealing with Errors
If there was any problem with the execution of a command, the bot will attempt to diagnose it and let you know of any modifications that need to be made to the command.